m (Gelthor moved page Turing Complete/Equality to Level/Equality without leaving a redirect) |
(Added infobox) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Header Nav|game=Turing Complete}} | {{Header Nav|game=Turing Complete}} | ||
{{Infobox level | |||
| section = CPU Architecture 2 | |||
| type = Component | |||
| prerequisite1 = Byte Constant | |||
| unlocks-level1 = Unsigned Less | |||
| unlocks-level2 = Signed Less | |||
| unlocks-component1 = Equal | |||
| scored = Yes | |||
| highscore = 40 | |||
| api-enum-id = byte_equal | |||
| api-enum-number = 70 | |||
}} | |||
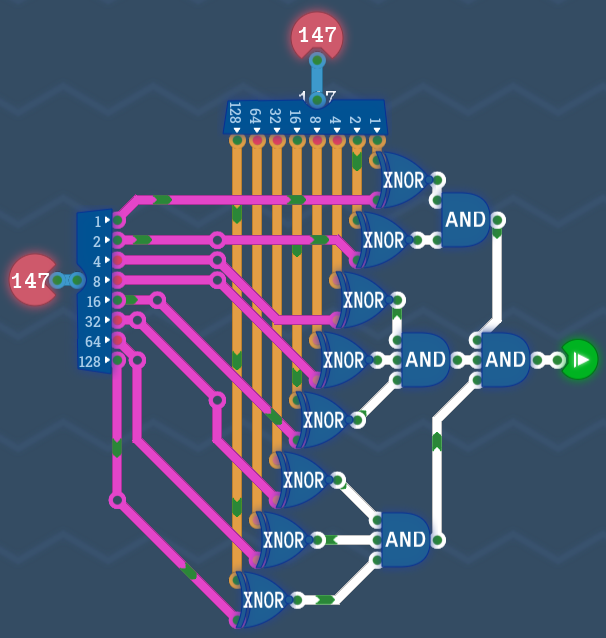
This level has you create a circuit that checks if two 8-bit values are identical. | This level has you create a circuit that checks if two 8-bit values are identical. | ||
Latest revision as of 16:05, 23 August 2024
| Section | CPU Architecture 2 |
|---|---|
| Type | Component |
| Prerequisite | Byte Constant |
| Unlocks | Unsigned Less Signed Less |
| Equal | |
| Scored | Yes |
| High score | 40 |
| API | byte_equal (70) |
This level has you create a circuit that checks if two 8-bit values are identical.
One way to do this is to figure out how to check if two bits are identical and then scale that up. And there is a gate for that job, the XNOR Gate.
So, this becomes a matter of using two Byte Splitters to get the raw bits and then putting down an XNOR Gate for each pair. Then just use And Gates to check that all bits are equal.